Fixed vs Variable Expenses: Balancing Your Budget
Reading Time: 4 minutesDo you ever find yourself wondering where all your income goes? If budgeting is an impossible puzzle, understanding the difference between fixed and variable expenses is a crucial first step toward financial control. In this blog post, we discuss fixed vs variable expenses and provide practical advice for managing both, helping you construct a budget that works for you.
Table of content
- What are fixed expenses?
- What are variable expenses?
- Fixed vs variable expenses: The differences
- Budgeting for fixed and variable expenses
- Building a Balanced Budget
What are Fixed Expenses?
Fixed expenses are the costs that remain constant each month. You can predict and plan for these expenses, such as:
- Rent or mortgage payments: Your living space or business premises cost the same monthly amount.
- Insurance premiums: Whether it’s for your car, health, or business, insurance costs tend to stay steady.
- Loan repayments: If you have a fixed-rate loan, the monthly repayments won’t change.
Imagine you’re running a digital marketing agency. Your fixed expenses include rent for your office space, expenses for full-time employees, insurance premiums, subscription fees for essential software tools, and utilities like electricity and internet. These expenses don’t fluctuate significantly from month to month, regardless of how many clients you acquire or the level of business activity.
Understanding fixed expenses is crucial for financial planning and budgeting, as they provide a stable baseline of costs that must be covered monthly. You can allocate resources efficiently, ensure financial stability, and make informed decisions about investments and growth opportunities.
What are Variable Expenses?
Understanding how fixed expenses differ from variable expenses is crucial. While fixed expenses remain constant, variable expenses fluctuate based on business activity or personal choices.
Examples of variable expenses are:
- Utility bills: These can fluctuate based on usage and seasonal changes.
- Raw materials: For businesses, the cost of goods can vary depending on market prices.
- Entertainment and dining out: Personal choices that can be adjusted as needed.
For instance, in a marketing agency, variable expenses might include advertising costs, freelance fees for project-based work, and travel expenses for client meetings. Similarly, in personal finances, variable expenses could include groceries, entertainment, dining out, and shopping.
Keeping a close eye on variable expenses and adjusting them based on sales and production levels is an effective way to optimize costs, maximize profit margins, and adapt to changes in the market. By analyzing trends in variable expenses, you can gain valuable insights into performance and identify opportunities for growth and improvement.
Fixed vs Variable Expenses: The Differences
Here’s a table summarizing the differences between Fixed and Variable expenses in the context of a small business:
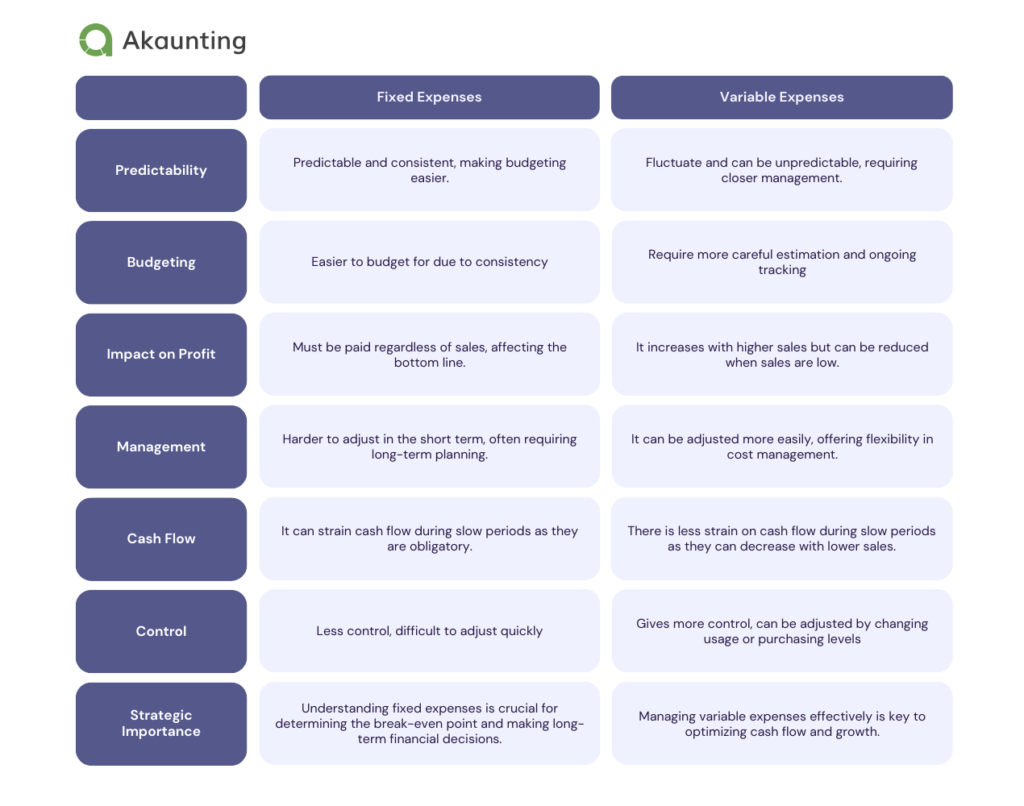
Basically, fixed expenses provide stability but can be a burden during downturns. On the other hand, variable expenses offer flexibility but require active management to maintain profitability.
Budgeting for Fixed and Variable Expenses
A meticulous approach to budgeting for fixed and variable expenses ensures financial obligations are met while allowing flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions.
Here are budgeting tips to consider:
- Identify and List Expenses: Determine which business expenses are fixed or variable.
- Analyze Past Spending: Review the past year’s bank statements, receipts, and financial statements to estimate monthly costs for fixed and variable expenses.
- Create a Budget Framework: Use a spreadsheet or budgeting app to list all expenses. Allocate a specific amount for fixed expenses, which are predictable. Estimate variable expenses based on historical data, adjusting for expected changes in business activity.
- Monitor Cash Flow: It is important to regularly compare actual expenses against the budget and make monthly adjustments based on sales/service levels.
- Plan for Seasonal Fluctuations: Adjust the budget for higher variable expenses during peak seasons.
- Maintain a Reserve Fund: Set aside a portion of profits to cover unexpected increases in variable expenses or shortfalls in revenue.
- Regularly Review and Adjust: At least quarterly, review the budget and adjust for any significant changes in fixed costs or business operations.
- Cost-Control Measures: Implement cost-saving measures for variable expenses, like negotiating better rates with suppliers or reducing energy consumption.
- Use Forecasting: Forecast future sales and expenses to make informed decisions about purchasing and inventory management.
- Leverage Technology: Use financial management tools for monitoring real-time expenses and cash flow. Akaunting’s expense management feature helps you track expenses effectively, ensuring your business is not at risk of poor financial management.
Building Your Balanced Budget
When managing your finances, a popular method is to follow the 50/30/20 rule.
This rule suggests that you allocate 50% of your income towards your needs, 30% towards your wants, and 20% towards your savings. Needs refer to fixed expenses essential for survival, such as rent, utilities, and groceries.
On the other hand, Wants refer to variable expenses that are not essential but improve your quality of life, such as dining out, entertainment, and travel. While the 50/30/20 rule provides a good framework, it’s important to personalize it based on your income and goals.
For instance, if you have a high debt, you may need to allocate more towards your savings and reduce your wants. Similarly, you may need to adjust your allocations accordingly if you save for a specific goal, like a down payment on a house.
What Next…
Understanding fixed vs. variable expenses puts you in the driver’s seat of your finances. You can build a budget supporting your business goals and financial stability by actively managing expenses and using the right tools.
Akaunting provides a customizable expense management feature that saves you time on expense recording, tracking, and budgeting
Financial success is a journey; every step towards better budgeting is a win.




